

There are three types of alternator failures: short, open (wire burned out), or loss in rotor magnetism. A short or open in one of the coil wires will result in either a low output, or no output at all. A loss in rotor magnetism, which may be caused by dropping or hitting the alternator, by leaving it near an electromagnetic field, or just by aging, will result in low output.
Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
Remove the left upper inner fairing (see Upper Inner Fairing Removal in the Frame chapter).
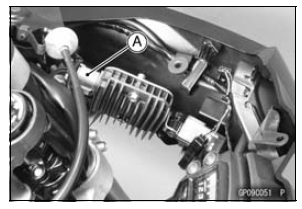
Disconnect the alternator lead connector [A].
Connect the hand tester as shown in the table 1.
Special Tool - Hand Tester: 57001-1394
Start the engine.
Run it at the rpm given in the table 1.
Note the voltage readings (total 3 measurements).
Table 1 Alternator Output Voltage at 4 000 r/min (rpm)
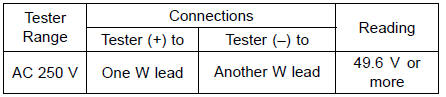
If the output voltage shows the value in the table, the alternator operates properly. The regulator/rectifier is damaged.
If the output voltage shows a much lower reading than that given in the table, stop the engine and inspect the stator coil resistance.
Stop the engine.
Connect the hand tester as shown in the table 2.
Special Tool - Hand Tester: 57001-1394
Table 2 Stator Coil Resistance at 20°C (68°F)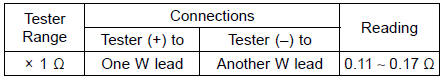
If there is more resistance than shown in the table, or no hand tester reading (infinity) for any two leads, the stator has an open lead and must be replaced. Much less than this resistance means the stator is shorted, and must be replaced.
Any hand tester reading less than infinity (∞) indicates a short, necessitating stator replacement.
If the stator coil has normal resistance, but the voltage check showed the alternator to be defective; then the rotor magnets have probably weakened, and the rotor must be replaced.
 Charging Voltage Inspection
Charging Voltage Inspection Regulator/Rectifier Inspection
Regulator/Rectifier InspectionOil Seal, Grease Seal
Do not remove pressed oil or grease seals unless removal
is necessary. Replace with new ones whenever removed.
Press new oil seals with manufacture and size marks facing
out. Make sure the seal is aligned properly when installing.
Apply specified grease to the lip of seal before installing ...
Oil Pressure Switch Installation
Using a high flash-point solvent, clean off any oil or dirt
that may be on the silicone sealant coating area. Dry
them with a clean cloth.
Apply silicone sealant to the threads of the oil pressure
switch, and tighten it.
Sealant - Liquid Gasket, TB1211: 56019-120
Torque - Oil Pressure ...
Lubrication
Lubrication is necessary after riding
through rain or on wet roads, or any
time that the chain appears dry.
Use a lubricant for sealed chains to
prevent deterioration of chain seals. If
the chain is especially dirty, clean it
using a cleaner for sealed chains following
the instructions suppli ...